
Each strand has a conformation resembling that of poly-L-proline 7 in a extended helical conformation where all of the bonds are trans to each other (poly-L-proline II). The collagens are a unique class of proteins, which have three chains that wrap together in a triple helix. Proteins with well-defined antiparallel β-pleated sheets (β-helices) have negative bands at 218 nm and positive bands at 195 nm 5, while disordered proteins have very low ellipticity above 210 nm and negative bands near 195 nm 6. For example, α-helical proteins have negative bands at 222 nm and 208 nm and a positive band at 193 nm 4. The result is that different structural elements have characteristic CD spectra ( Figure 1a). When the chromophores of the amides of the polypeptide backbone of proteins are aligned in arrays, their optical transitions are shifted or split into multiple transitions due to “exciton” interactions (See Sreerama and Woody 3 for a recent review). ĬD is an excellent method of determining the secondary structure of proteins. There is also a website that illustrates the production of circularly polarized light and the circular dichroism of optically active molecules with animated graphics. For illustrations of the phenomena of CD see Beychok 2. CD is reported either in units of ΔE, the difference in absorbance of E R and E L by an asymmetric molecule, or in degrees ellipticity, which is defined as the angle whose tangent is the ratio of the minor to the major axis of the ellipse. The result is that the plane of the light wave is rotated and that the addition of the E R and E L vectors results in a vector that traces out an ellipse and the light is said to be elliptically polarized. When asymmetric molecules interact with light, they may absorb right and left handed circularly polarized light to different extents (hence the term circular dichroism) and also have different indices of refraction for the two waves. The waves are 90 degrees out of phase with each other and can be separated using a variety of prisms or electronic devices which utilize Pockel's effect 1. The two circularly polarized waves have physical existence. When viewed from the front, the sinusoidal wave can be visualized as the resultant of two vectors of equal length, which trace out circles, one which rotates clockwise (E R) and the other which rotates counterclockwise (E L). If the light is polarized by passing through suitable prisms or filters its electric field, E, will oscillate sinusoidally in a single plane.
A beam of light has time dependent electric and magnetic fields associated with it. Briefly, circular dichroism is defined as the unequal absorption of left-handed and right-handed circularly polarized light. Circular dichroism (CD) is an excellent method for rapidly evaluating the secondary structure, folding and binding properties of proteins.
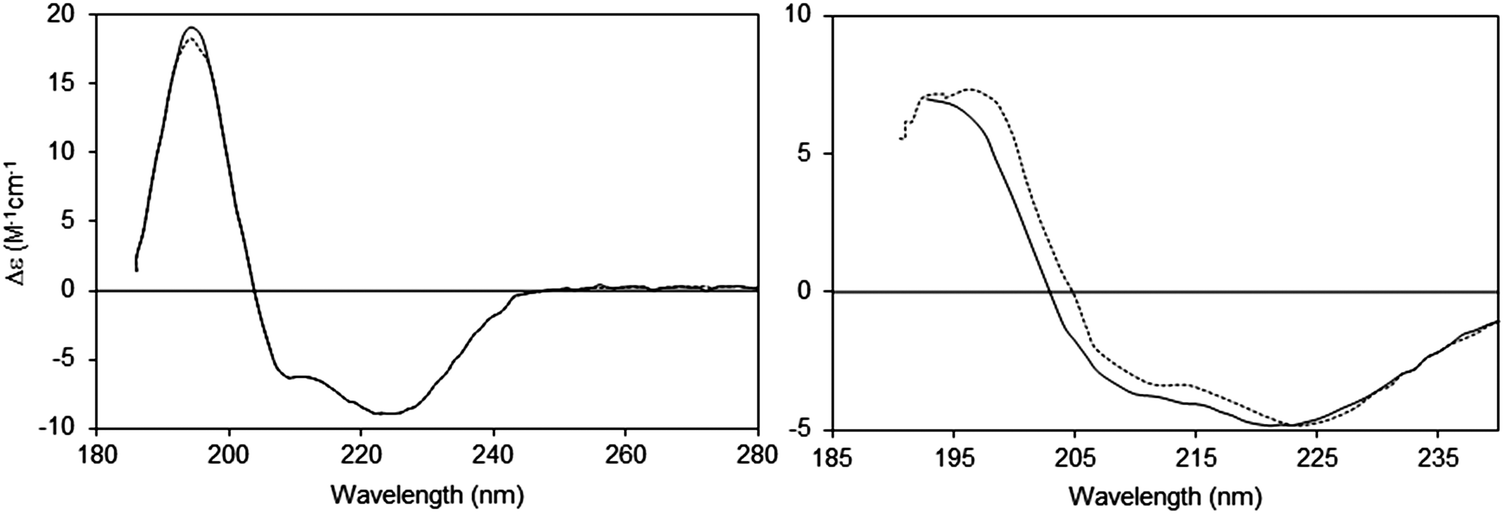
The rapid characterization of new proteins is of great importance for the fields of proteomics and structural genomics.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
